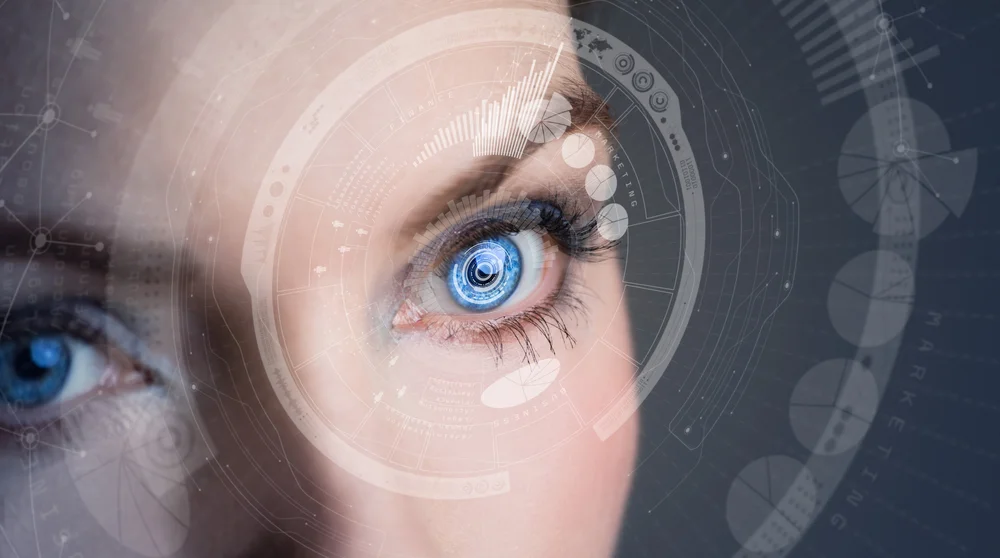
Retina Scan
As the overwhelming majority of both financial and non-financial private spaces and systems either move entirely to or at least get connected in major part with the digital world, research, and development into making these systems more secure is happening at breakneck speeds.
After the innovations of facial recognition and accurate fingerprint scanning in biometric verification technology, a new innovation that has come to the forefront is the retina scan. The nature of these scans makes them some of the most secure possible authentication methods and are thus used in the highest-level security spaces.
What is a Retina Scan?
Retina scanning is a form of biometric authentication technology that utilizes the intricacies of the human eye to identify an individual. In particular, the pattern formed by the blood vessels inside the retina of the individual is used as a unique identifying trait for this system.
These tools rely on a special tool known as a retina scanner for this purpose. The scanner emits a beam of low-energy infrared light into the person’s eye, the deformation and bouncing of the light is what reveals the unique patterns of the person’s blood vessels.
The scanner captures this pattern and records it in the form of a digital image, to be used for identification and authentication. At this point, just like any other biometric verification system it compares against a database of similarly captured and saved images to see if the input matches one of them.
Retina Scan vs Iris Recognition
Another very prominent form of biometric authentication that works off of the unique nature of the human eye is iris recognition. It is thus important to differentiate between the two, as they can be confused quite easily.
In contrast to a retina scan, iris scans work to capture the unique patterns formed by the colored part of the eye. As this part of the eye is closer to the front compared to the retina, it can be performed at a slight distance of a few inches to a few feet, while retina scans require the person to bring their eye right up close to the scanner.
While both kinds of biometric verification have similarly low levels of false acceptance, retina scans are slightly more prone to false rejections because of the fact that certain diseases and conditions can affect the blood vessels.
Applications of Retina Scans
Now that we have talked about how retina scan biometrics work, let’s talk about how this tech is being implemented for security purposes.
Military and Defense
One of the most common use cases of retina scanning is in the world of military and defense installations. Many sensitive locations and spaces in military bases and defense buildings make use of a retina scan for security to prevent unauthorized access.
The extremely high level of accuracy that this kind of authentication provides, combined with the fact that it is exceptionally difficult (to say the least) to replicate the patterns of the blood vessels of an individual’s eye, means that it can be trusted for sensitive use cases.
In some cases, this tech has also been used in war zones to be able to identify individuals and differentiate civilians from malicious actors with a high level of precision, often combined with other forms of biometric verification to make absolutely sure that the wrong person is not held.
Financial Services
In certain services provided by banks and other financial institutions that are considered to be even more private and/or sensitive than general transactions, this technology is useful.
Banks will often use retina scanning as a form of authentication for safety deposit boxes for customers as well as for vaults. The use of this method ensures that the potentially highly valuable goods or documents that are often stored in these containers are only accessed by those who are allowed access.
Many financial institutions also utilize this form of biometric authentication to secure and protect their internal systems and data centers, which in the modern digital world form the core of their enterprise.
Healthcare
Retina scans are sometimes used in hospitals for accurate patient identification. This helps to make sure that the medical professionals who are helping an individual are aware of potential health problems, allergies, and other important information that can help them to provide better care to the individual.
A retina scanner can also be used to check the health of the eye of a patient, potentially detecting some illnesses and diseases of the eyes by looking at the blood vessels.
Conclusion
In the modern world of digital authentication, biometric verification technologies have advanced to the point where the eye of the person can work as their most accurate identifier. The high level of accuracy and security that retina scan provide makes them suitable for use in the most sensitive of locations and use cases.
For More Details NCD!